Ever wondered why some websites consistently rank higher in search results and attract tons of visitors? The secret lies in keyword research in SEO—the foundation of every successful digital marketing strategy.
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about keyword research—from understanding keywords to finding the best ones to grow your website traffic. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to sharpen your SEO skills, let’s get started.
Table of Contents
- From words to reach: Understanding Keywords easily
- Keyword Research in SEO: The First Step to Mastery
- How to do keyword research in SEO?
- Why Is Keyword Research Important in SEO?
- How Does Keyword Research Actually Work?
From words to reach: Understanding Keywords easily
What are keywords?
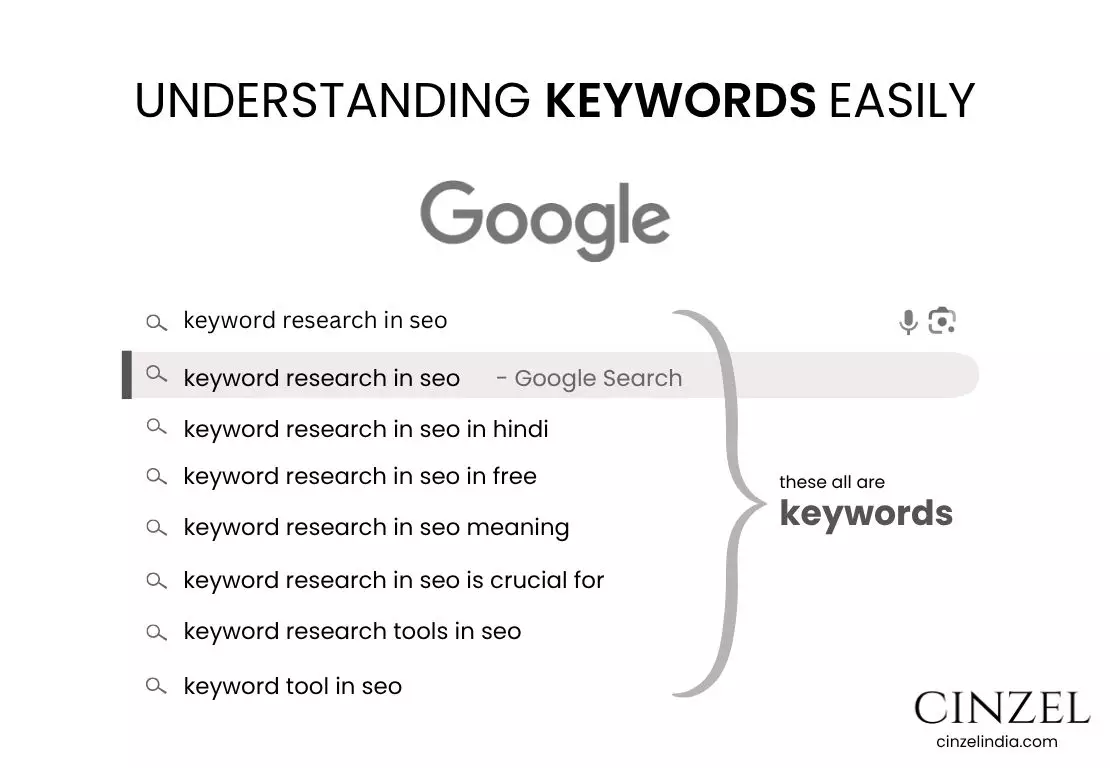 Keywords are specific words or phrases that users enter into search engines when searching for information, products, or services. For instance, a phrase like “keyword research in SEO” is considered a keyword. Selecting the right keywords ensures your content reaches the right audience effectively.
Keywords are specific words or phrases that users enter into search engines when searching for information, products, or services. For instance, a phrase like “keyword research in SEO” is considered a keyword. Selecting the right keywords ensures your content reaches the right audience effectively.
Types of Keywords You Must Know
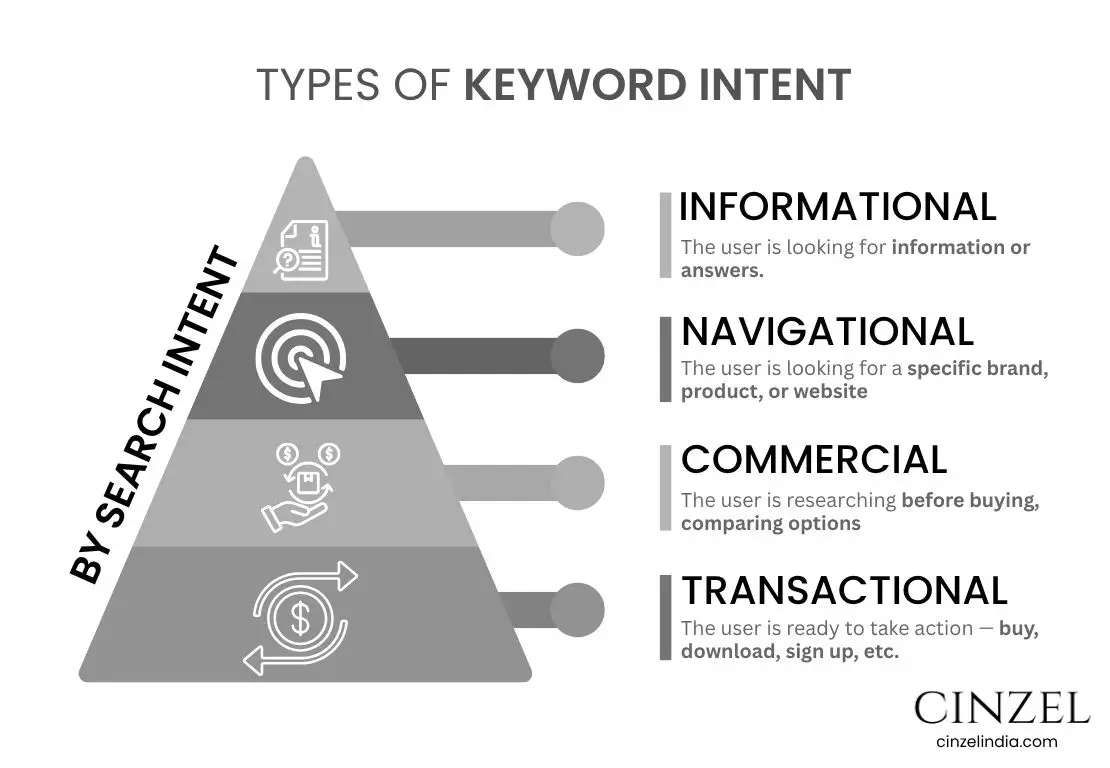 1. By Searcher Intent
1. By Searcher Intent
Searcher intent describes why someone is searching — their goal or purpose behind the keyword. This allows you to tailor your content to match what users are looking for.
a) Informational Keywords
-
-
The user is seeking knowledge or solutions.
-
Common with "how to", "what is", "guide", "tips", etc.
-
Examples:
-
-
"how to use aloe vera for acne"
-
"benefits of green tea"
-
"what is digital marketing"
-
Best for: Blog posts, guides, tutorials
b) Navigational Keywords
-
-
The user is searching for a particular brand, item, or web page.
-
They already know where they want to go.
-
Examples:
-
-
"Nike official site"
-
"Facebook login"
-
"Amazon India"
-
Best for: Brand awareness, branded search
c) Commercial Keywords
-
-
The user is researching before buying, comparing options.
-
Usually includes terms like “best,” “top,” “reviews,” “vs.”
Examples:-
"best face wash for oily skin"
-
"Samsung vs iPhone"
-
"top 10 gaming laptops"
-
-
Best for: Product roundups, review blogs, comparison posts
d) Transactional Keywords
-
-
The user is ready to take action — buy, download, sign up, etc.
-
Includes action words like “buy,” “discount,” “order,” “download.”
-
Examples:
-
-
"buy smartwatch online"
-
"download resume template"
-
"book hotel near Delhi airport"
-
Best for: Product pages, landing pages, ads
2. By Keyword Length and Specificity
This describes the level of generality or specificity of a keyword.
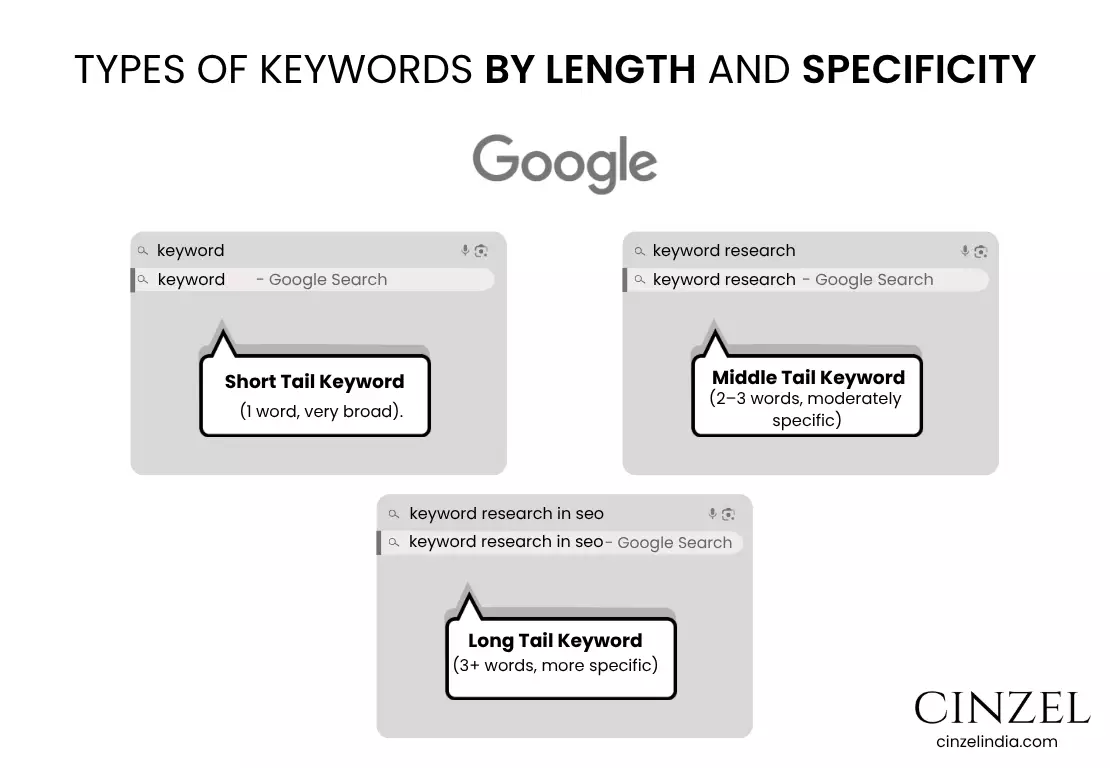
a) Short-Tail Keywords (Head Keywords)
-
-
1–2 words, very broad.
-
Large number of searches, strong competition, but fewer conversions.
-
Examples:
-
-
“laptops”
-
“shoes”
-
“marketing”
-
Use when: You want wide visibility but need strong SEO to rank.
b) Middle-Tail Keywords (Body Keywords)
-
-
2–3 words, moderately specific.
-
Medium search volume, medium competition, better conversion rate than short-tail.
-
Examples:
-
-
“gaming laptops”
-
“running shoes”
-
“digital marketing”
-
Use when: You want a balance between search volume and relevance, making it easier to rank and convert compared to short-tail keywords.
c) Long-Tail Keywords
-
-
3+ words, more specific.
-
Lower search volume, but higher intent and conversion.
-
Examples:
-
-
“best gaming laptops under 60000”
-
“organic shampoo for hair fall control”
-
Use when: Targeting a specific audience or niche.
d) LSI Keywords (Latent Semantic Indexing Keywords)
-
-
These are thematically related keywords — not synonyms, but conceptually linked.
-
Assist Google in interpreting the meaning and relevance of your content.
-
Examples:
For the keyword “digital marketing,” LSI keywords could be:
-
-
“SEO,” “email marketing,” “content strategy,” “online advertising”
-
Use when: Optimizing content to boost SEO without keyword stuffing.
3. Other Important Keyword Categories
These keywords play specific roles in SEO, PPC, or branding.
a) Branded Keywords
-
-
Include a brand name in the search.
-
Useful for tracking brand awareness and targeting brand-loyal customers.
Examples:
-
-
“Nike running shoes”
-
“Mamaearth face wash review”
-
b) Geo targeted Keywords
-
-
Include location-based terms.
-
Ideal for targeting local SEO and region-based products or services.
-
Examples:
-
-
“best pizza in Noida”
-
“wedding photographer in Delhi”
-
c) Primary Keywords
-
-
The primary keyword you aim to have your page or content rank in search results.
-
Used in title, URL, H1, meta description, etc.
-
Example:
For a page selling aloe vera gel, the primary keyword might be:
-
-
“aloe vera gel for face”
-
d) Secondary Keywords
-
-
Related or supporting terms that help enrich your content.
-
Can be long-tail or LSI keywords.
-
Examples:
-
-
"natural skin moisturizer", "soothing gel for sunburn"
-
e) Seed Keywords
The starting keywords used to begin your keyword research.
-
-
They are general and form the base for finding more specific keywords.
-
Examples:
-
-
"skincare", "digital marketing", "laptops"
-
Use in: Keyword tools to generate keyword ideas.
Keyword Research in SEO: The First Step to Mastery
What is keyword research in seo?
Keyword research involves identifying and analyzing the terms people search for online. It's a crucial part of SEO that reveals user intent and popular queries, helping businesses create targeted content. By using the right keywords, companies can boost search rankings, attract relevant traffic, and strengthen their overall digital marketing strategy for better visibility and engagement.
Why Is Keyword Research Important in SEO?
1. Understand What Your Audience is Searching
-
-
Helps you identify the specific words and phrases your audience uses when searching online.
-
Aligns your content with their needs and interests.
-
2. Drive Quality Organic Traffic
-
-
Targeting the right keywords means more relevant visitors who are interested in your product, service, or information.
-
Increases chances of conversions and engagement.
-
3. Boost Your SEO Ranking
-
-
Google uses keywords to understand content relevance.
-
Proper keyword use improves your chances of ranking higher in search engine results pages (SERPs).
-
4. Outrank Competitors
-
-
Helps you find low-competition or untapped keywords.
-
Gives you a chance to appear above your competitors in search results.
-
5. Create Valuable & Intent-Focused Content
-
-
Ensures you’re answering real user questions.
-
Assists in organizing content according to informational, transactional, or navigational search intent.
-
6. Guide Your Content Strategy
-
-
Acts as the foundation for blog posts, landing pages, ads, and product descriptions.
-
Keep your content creation focused and strategic.
-
7. Improve ROI on Marketing Efforts
-
-
Drives targeted traffic that’s more likely to convert.
-
Saves time and resources by focusing on what actually works.
-
How Does Keyword Research Actually Work?
1. Discovering Relevant Keywords:
Start by exploring and identifying search terms that are closely related to your products, services, or industry through brainstorming and research.
2. Evaluating Keyword Metrics:
Use SEO tools to assess how frequently a keyword is searched (search volume), how hard it is to rank for (keyword difficulty), and other key insights like cost-per-click (CPC).
3. Selecting the Right Keywords:
Based on your research, choose the keywords that best match your goals—balancing relevance, popularity, and competition levels.
4. Content Optimization:
Incorporate the selected keywords strategically into website content, such as headings, meta tags, and body copy, to enhance visibility in search engines.
5. Monitoring and Improving:
Keyword research in seo doesn’t end after implementation. Keep an eye on performance, track rankings, and continuously refine your keyword strategy for better results.
How to do keyword research in seo?
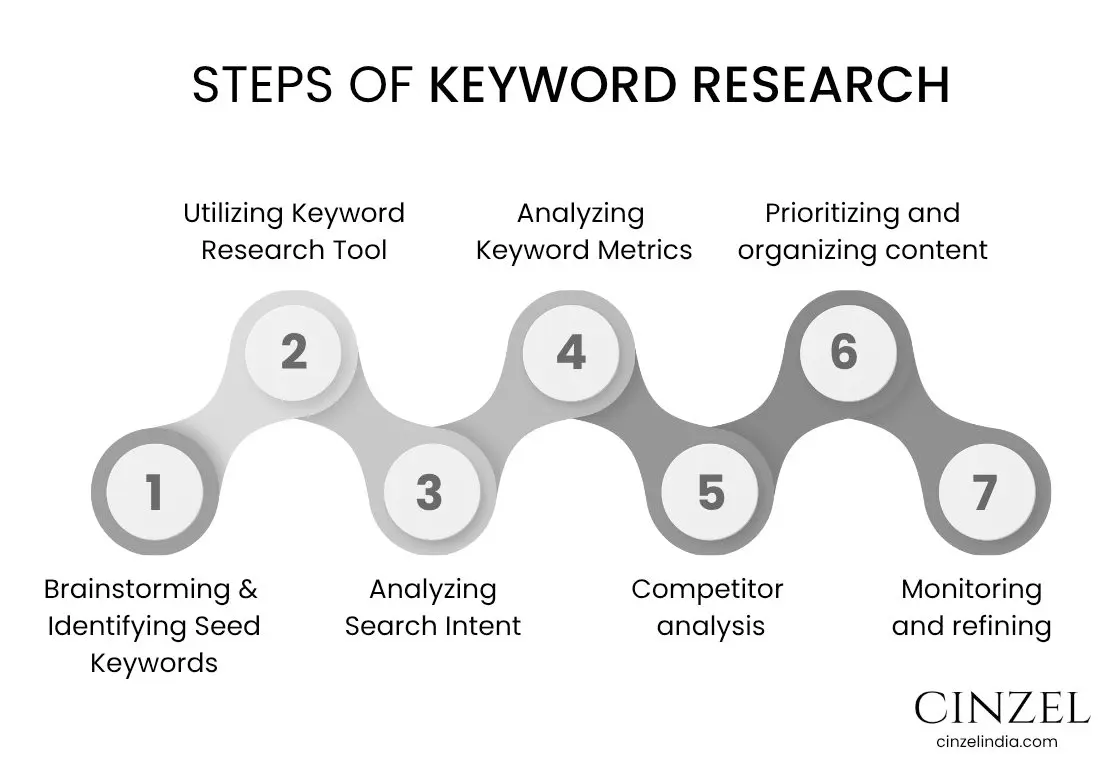 1. Brainstorming and Identifying Seed Keywords:
1. Brainstorming and Identifying Seed Keywords:
Start with Your Business Core
-
-
-
Think about what your business offers: products, services, or content.
-
Ask yourself: “What would I search on Google if I needed this?”
-
Consider brand terms, industry terms, and customer pain points.
-
-
Create Topic Buckets
-
-
-
Group your ideas into general categories or core themes.
-
These might include different service categories, product types, or content areas.
-
Example: For a digital marketing agency – SEO, PPC, social media, content marketing.
-
-
Identify Seed Keywords
-
-
-
Seed keywords are short, general keywords that represent each topic bucket.
-
They are usually 1–2 words long and help generate more specific keyword ideas later.
-
Example: From the topic “SEO,” seed keywords might be “SEO tools,” “SEO tips,” or “search engine optimization.”
-
-
Use Customer Language
-
-
-
Think from the perspective of your target audience.
-
Use terms your customers actually use, not just industry jargon.
-
-
Leverage Competitor Websites
-
-
-
Explore competitors' websites or blogs to see what keywords and topics they’re targeting.
This can inspire your own list of seed keywords.
-
-
Make a Master List
-
-
-
Compile all seed keywords in one document or spreadsheet.
-
This forms the base for deeper keyword research using tools later on.
-
-
2. Utilizing Keyword Research Tool:
Google Keyword Planner
-
-
-
What it is: A free keyword research tool provided by Google, primarily used by advertisers for Google Ads but extremely useful for SEO as well.
-
Key Features:
-
Search volume data: Shows how many people search for a particular keyword each month.
-
Keyword suggestions: Generates new keyword ideas based on a seed keyword or website URL.
-
Competition level: Indicates how competitive a keyword is for paid search (can give some insight for SEO too).
-
-
How to use it:
-
Enter a seed keyword to generate keyword ideas.
-
Analyze monthly search volumes to find high-potential keywords.
-
Filter by location, language, and search network for more precise results.
-
-
-
Search Engine Suggestions
a.) Google Autocomplete
-
-
-
As you type in the Google search bar, it predicts what you might be searching.
-
-
How it helps:
-
-
-
-
Reveals actual phrases people are typing.
-
Useful for discovering popular long-tail keywords.
-
Helps uncover search intent behind a query.
-
-
-
b.) People Also Ask (PAA)
-
-
-
Found in many search results, showing common related questions.
-
-
How it helps:
-
-
-
-
Understands user concerns and questions.
-
Great source of content ideas and FAQ keywords.
-
Reflects user intent and offers conversational keyword opportunities.
-
-
-
3. Analyzing Search Intent:
Search intent, also known as user intent, is the purpose behind a user's search — what they truly want to discover or accomplish.
Understanding intent helps create content that directly satisfies the user’s needs.
Types of Search Intent-
-
-
-
Informational Intent
-
“What is SEO?”
-
“How to start a blog?”
-
Purpose: The user is looking for information or answers.
Examples: -
Content Strategy: Use blog posts, how-to guides, explainer articles, and videos.
-
-
Navigational Intent
-
-
-
“Facebook login”
-
“Nike shoes official site”
-
Purpose: The user wants to find a specific website or brand
Examples: -
Content Strategy: Make sure your brand and key pages are well-optimized and easy to find.
-
-
Transactional Intent
-
-
-
“Buy iPhone 14 online”
-
“Book flight to Delhi”
-
Purpose: The user is ready to make a purchase or take an action.
Examples: -
Content Strategy: Use product pages, service landing pages, pricing info, and clear CTAs (calls to action).
-
-
Commercial Intent (Investigation)
-
-
-
“Best laptops under 50000”
-
“Ahrefs vs SEMrush comparison”
-
Purpose: The user is researching before making a purchase.
Examples: -
Content Strategy: Create comparison articles, reviews, testimonials, and feature breakdowns.
-
-
4. Analyzing Keyword Metrics
It involves evaluating the quantitative data behind each keyword to determine how valuable or feasible it is for your SEO or PPC strategy. These metrics help you choose the right keywords to target.
1. Search Volume
It refers to the number of times a specific keyword or phrase is searched on a search engine like Google within a given timeframe—typically monthly. It's a key metric in keyword research and SEO strategy, helping marketers understand how popular (or in-demand) a keyword is among users.
For example:
The keyword "best smartphones 2025" might have a search volume of 10,000/month, meaning it's searched 10,000 times every month.
Factors That Influence Search Volume :
1. Seasonality:
Search volume often rises or falls based on the time of year. For example, keywords like "Christmas gifts" peak in December.
2. Trends:
Popular culture, news, or social media trends can cause sudden spikes in keyword searches. A viral topic can temporarily boost search volume.
3. Advertising:
Heavy advertising or product launches can increase awareness, leading more people to search for related keywords.
4. SEO Efforts:
When many websites start optimizing for a particular keyword, it can boost its visibility and lead to more searches over time.
5. User Behavior:
Changes in how people search—such as increased voice search or mobile use—can shift which keywords are searched and how often.
2. Keyword Difficulty (KD) or SEO Difficulty
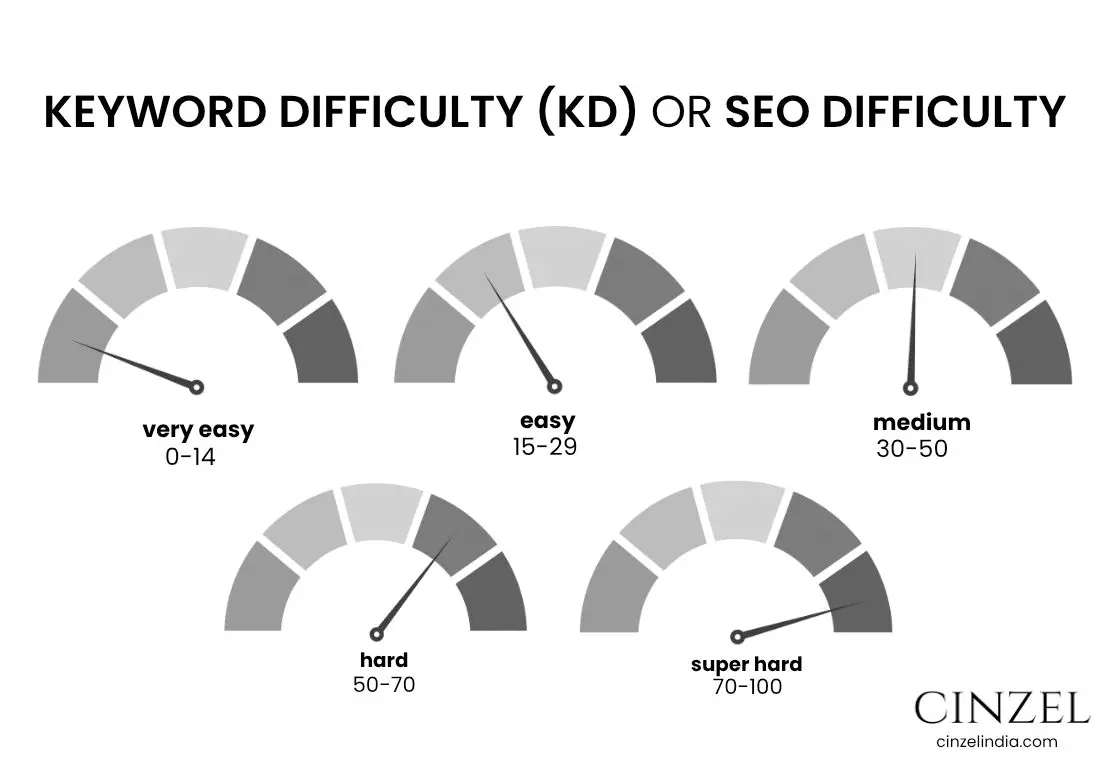
Keyword Difficulty (KD) indicates how challenging it is to achieve a first-page ranking on Google for a given keyword.. It considers factors like competition, domain authority, and content quality of top-ranking pages.
How to Check Keyword Difficulty?
Use SEO tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, Moz, or Ubersuggest. Enter your target keyword, and the tool will give a KD score (usually from 0 to 100), along with other metrics like search volume and SERP competition.
What are the Solutions for Keyword Difficulty?
-
-
-
Target long-tail, low-difficulty keywords for quicker wins.
-
Improve content quality and depth to outrank competitors.
-
Build high-quality backlinks to boost authority.
-
Focus on user intent and semantic SEO.
-
-
3. CPC (Cost-Per-Click)
-
-
The average amount advertisers pay for a click when running ads on that keyword.
-
Why it matters: Shows the commercial value or buying intent behind the keyword.
-
Tip: High CPC often means high transactional intent and strong competition.
-
4.Click-Through Rate (CTR) Potential
-
-
An estimate of how many people actually click on organic results for that keyword.
-
Why it matters: Some keywords may have low organic CTR due to too many ads, featured snippets, or answer boxes.
-
Tip: Choose keywords with higher CTR potential for better organic traffic.
-
5.Trend Over Time
-
-
Shows how keyword interest changes over time (seasonal or long-term trends).
-
Why it matters: Helps you plan timely content and campaigns.
-
Tool: Use Google Trends to check seasonality or growth.
-
6. Keyword Relevance
-
-
-
How closely a keyword matches your content, product, or audience’s intent.
-
Why it matters: Relevant keywords result in better engagement, lower bounce rates, and more conversions.
-
Tip: Don’t chase high volume if the keyword doesn’t match your offering.
-
-
7. SERP Features Presence
-
-
Indicates if the keyword activates special elements in Google’s results, such as featured snippets, maps, images, or videos.
-
Why it matters: SERP features can impact visibility and your chance to get clicks.
-
Tip: Identify if your content type (e.g., video or listicle) fits the SERP layout.
-
Analyzing your competitors’ keyword strategies is a powerful way to uncover content opportunities and SEO gaps. It helps you understand what’s working in your niche and where you can outperform them with better content or targeting.
5. Competitor analysis
-
- Identify Competitors:
Utilize tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Google search to identify websites ranking for your desired keywords.These are your SEO competitors, not just business rivals. - Analyze Their Content:
Study their top-ranking pages. Look at keyword usage, content type, length, visuals, internal linking, and update frequency to see what works. - Find Content Gaps:
Use Keyword Gap tools to uncover topics your competitors missed or poorly covered.Focus on low-competition, high-intent keywords to gain a competitive advantage.
- Identify Competitors:
6. Prioritizing and organizing content
-
- Categorize Keywords
Group related keywords into themes (e.g., product types, blog topics, user intent like informational or transactional) to simplify planning and content targeting. - Prioritize Keywords
Focus on keywords that have a good mix of search volume, relevance, and low to medium difficulty. Also, consider their potential to
- Categorize Keywords

